The pancreas is an organ located in the abdomen. It plays an essential role in converting the food we eat into fuel for the body's cells.
Exocrine system incudes : Lacrimal glands (tear glands), Mammary glands, Mucous membranes, Prostate, Salivary glands, Sebaceous (oil) glands, Sweat glands, etc.
Endocrine system includes : Adrenal glands, Hypothalamus, Ovaries and testes, Parathyroid and thyroid gland, Pineal gland, Pituitary gland, and Thymus.
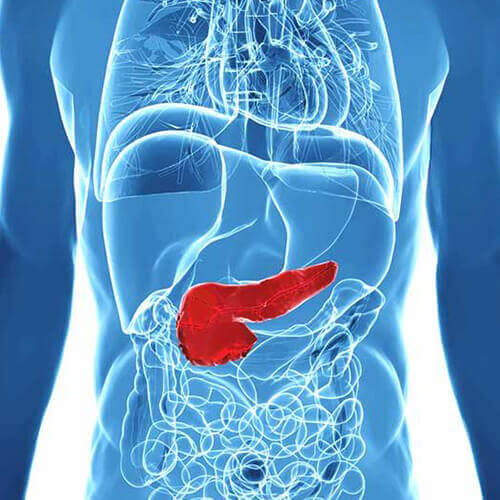
During digestion, your pancreas makes pancreatic juices called enzymes. These enzymes break down sugars, fats, and starches. Your pancreas also helps your digestive system by making hormones. These are chemical messengers that travel through your blood. Pancreatic hormones help regulate your blood sugar levels and appetite, stimulate stomach acids and tell your stomach when to empty.
Pancreatic enzymes : Your pancreas creates natural juices called pancreatic enzymes (Lipase, Protease, Amylase) to break down foods.
Pancreatic hormones : Insulin (maintains blood sugar), Glucagon (stimulates blood sugar level), Gastrin (stimulates gastric acid) and amylin (controls appetite and stomach emptying).
Pancreatitis - Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas that occurs when pancreatic enzyme secretions build up and begin to digest the organ itself. Acute pain attacks can last a few days, or chronic pain may develop over time.
Precursors to Pancreatic Cancer - Although the exact cause of pancreatic cancer is unknown, there are known risk factors that increase the risk. Cigarette smoking, a family history of pancreatic cancer or hereditary cancer syndromes, and chronic pancreatitis are some of these factors. Additionally, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) and pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasms (PanINs) are considered precursors to pancreatic cancer.
Pancreatic Cancer - Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is the most common form of pancreatic cancer, an exocrine tumor that arises from pancreatic duct cells. Approximately 5% of pancreatic tumors are endocrine tumors, sometimes called neuroendocrine tumors or islet cell tumors.
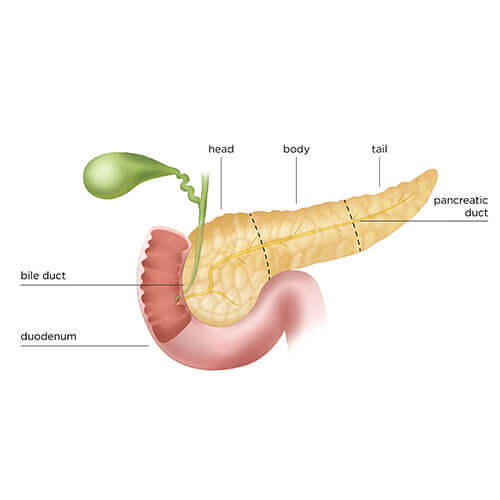

A Whipple procedure also known as a pancreaticoduodenectomy is a complex operation to remove the head of the pancreas, the first part of the small intestine (duodenum), the gallbladder and the bile duct. The Whipple procedure is used to treat tumors and other disorders of the pancreas, intestine and bile duct. It is the most often used surgery to treat pancreatic cancer that's confined to the head of the pancreas.